Hints Are Not Always Better
This week Steve Jones reminds us that improving performance in T-SQL is not always obvious. Those little nuggets of knowledge can be very handy, which is why you should be regularly looking to acquire more of them.
This week Steve Jones reminds us that improving performance in T-SQL is not always obvious. Those little nuggets of knowledge can be very handy, which is why you should be regularly looking to acquire more of them.
Today we have a guest editorial from Andy Warren. Andy talks about your annual review and how you might want to think about negotiating for a raise in advance.
The PATINDEX function of SQL Server packs powerful magic, but it is easy to get it wrong. Phil Factor returns to the Workbench format to give a tutorial of examples, samples and cookbook ideas to demonstrate the ways that this underrated function can be of practical use. It is intended to be pasted into SSMS and used as a basis for experiment.
If you make the decision to upgrade to 2008, there are a number of tools that make the process easier, but you still need to understand what things you should consider. We have a new article from Arshad Ali to help you understand the process and what you should consider.
This Friday Steve Jones wonders what types of bugs you find in software. Are there more prevalent because of design or coding?
Research firm The 451 Group coins "NewSQL" to categorize a new breed of database designed for distributed environments -- like the cloud.
Monitoring blocking can be problematic when you cannot catch it in the act. This article will show you an easy way to configure a SQL Server Profiler Trace to monitor blocking
Today we have a guest editorial from Andy Warren. Most people get an annual review that determines what their salary change might be for the next year. Does 3% make a difference? Andy Warren asks the question today.
SQL Server 2008 introduced many new functional and performance improvements for data warehousing, and SQL Server 2008 R2 includes all these and more. This paper discusses how to use SQL Server 2008 R2 to get great performance as your data warehouse scales up. We present lessons learned during extensive internal data warehouse testing on a 64-core HP Integrity Superdome during the development of the SQL Server 2008 release, and via production experience with large-scale SQL Server customers. Our testing indicates that many customers can expect their performance to nearly double on the same hardware they are currently using, merely by upgrading to SQL Server 2008 R2 from SQL Server 2005 or earlier, and compressing their fact tables. We cover techniques to improve manageability and performance at high-scale, encompassing data loading (extract, transform, load), query processing, partitioning, index maintenance, indexed view (aggregate) management, and backup and restore.
What do yo do if you find malicious code in your system? Delete it? Steve Jones suggests that a honeypot might be a better idea.
By Steve Jones
AI is a big deal in 2026, and at Redgate, we’re experimenting with how...
By Steve Jones
Another of our values: The facing page has this quote: “We admire people who...
By Ed Elliott
Running tSQLt unit tests is great from Visual Studio but my development workflow...
Comments posted to this topic are about the item No Defaults Passwords Ever
Hi, We have low latency high volume system. I have a table having 3...
Comments posted to this topic are about the item The Long Name
I run this code to create a table: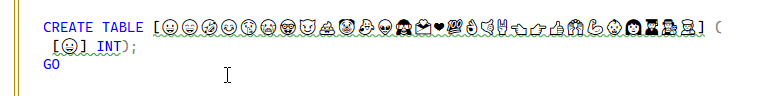 When I check the length, I get these results:
When I check the length, I get these results: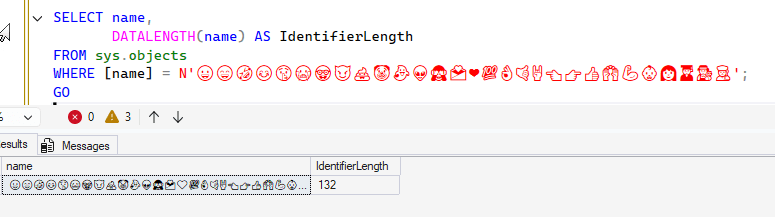 A table name is limited to 128 characters. How does this work?
A table name is limited to 128 characters. How does this work?