Article Overview
In this article we will learn how to integrate a Spring boot application with Apache Cassandra database and Redis cache. This is an extension to one of our previous articles which demonstrates the steps to set up Apache Cassandra and how to integrate is with Springboot, link shared below.
https://www.sqlservercentral.com/articles/cassandra-springboot-integration
In this tutorial we will use the same database and table from the above tutorial to complete the integration with Redis Cache.
Pre-requisites
Basic understanding of Springboot and Cassandra along with Cassandra database setup from the previous article. Recommendation is to go through the aforementioned tutorial before proceeding in this article.
Topics covered in this tutorial
- What is Redis Cache?
- How to install and start Redis?
- Redis Cli
- Springboot example with Apache Cassandra and Redis Cache
What is Redis Cache?
Redis or Remote Dictionary Server cache like any other caching mechanism is used to store data thereby reducing subsequent calls to the database thus improving the overall performance of the application. When a fetch request is received, application first looks for the data in Redis, if found it is returned from there else it goes to look in the database. Whenever a new record is fetched, it is cached in Redis against a corresponding key. When a DB update operation is performed, the Redis Cache also updates the result in its cache. Needless to say, for delete operation the data is deleted from the cache as well.
How to install Redis?
Windows 64bit Installation:
All versions of Redis can be downloaded from its official website
https://redis.io/download/
Unzip in a local folder and it should look as shown below:
To start the Redis server, double click on 'redis-server'. Default port is 6379.
Ubuntu Installation:
Please follow the instructions on the official site for installation https://redis.io/docs/getting-started/installation/install-redis-on-linux/
Redis CLI
The Redis CLI is a terminal program used to interact with the Redis Server, CLI stands for Command Line Interface. By default, redis-cli connects to the server at the address 127.0.0.1 with port 6379. To start double click on 'redis-cli' application available in the Redis package as shown above in the snapshot.
Visit https://redis.io/commands/ to learn about the commands.
Pre-requisites for Springboot example
- Java 8 or above
- IDE such as Eclipse/IntelliJ
- Postman
Overview - A Springboot application having two methods one post and one get to interact with Cassandra database. We use Postman as client to execute and test the operations. Next, we use Redis CLI to verify the entries in Redis Cache.
To begin with, let us setup a new Maven project in Eclipse. I used Spring boot's official website Spring initializr https://start.spring.io/ to generate a new project and then imported it in my eclipse workspace. The project structure is given below:
Pom.xml:
The following dependencies are required to integrate Spring boot application with Redis and Cassandra
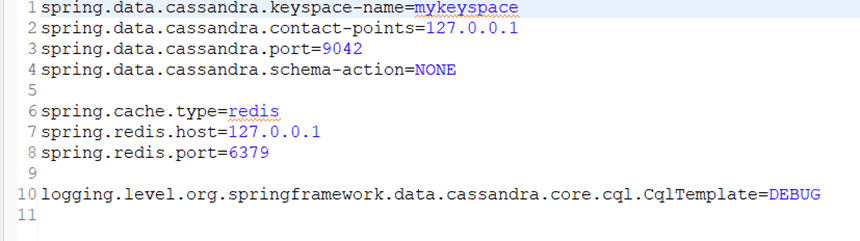
application.properties
Cassandra and Redis's configuration properties are declared here. Let us take a minute to study their configurations,
'keyspace-name' denotes the name of the Keyspace which was created in the above prerequisites section. 'Contact-points' denotes the end point for the host server, in this example it is localhost or 127.0.0.1. Default port for Cassandra is 9042. 'Schema-action=None' since no schema defined in this case.
'spring.cache.type' is redis as Redis cache is being used in this example, 'spring.redis.host' is once again localhost(127.0.0.1) and the default port for Redis is 6379.
The logging level for Cassandra is set to 'DEBUG', it will log the database queries in the console.
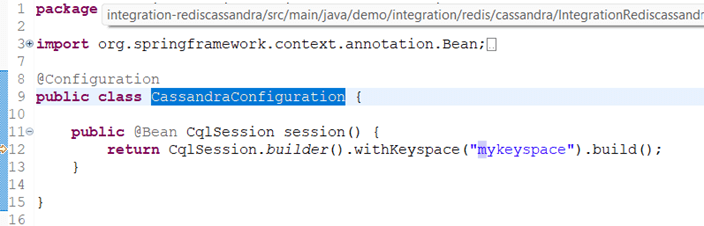
CassandraConfiguration.java
The Cassandra configuration class is used to get a session from the Keyspace.
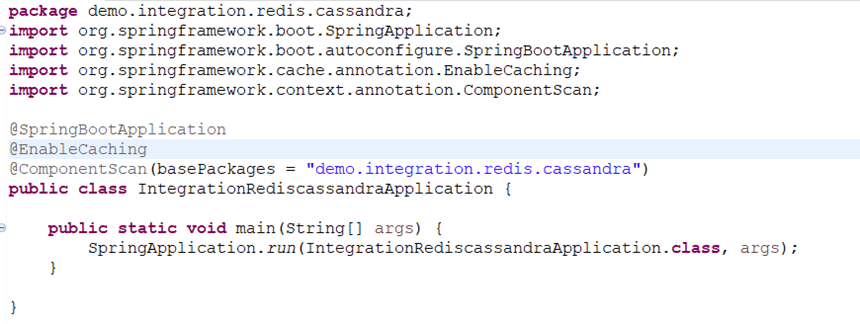
IntegrationRediscassandraApplication.java
This is the entry class of the application. @EnableCaching annotation is used to enable the caching mechanism in Spring.
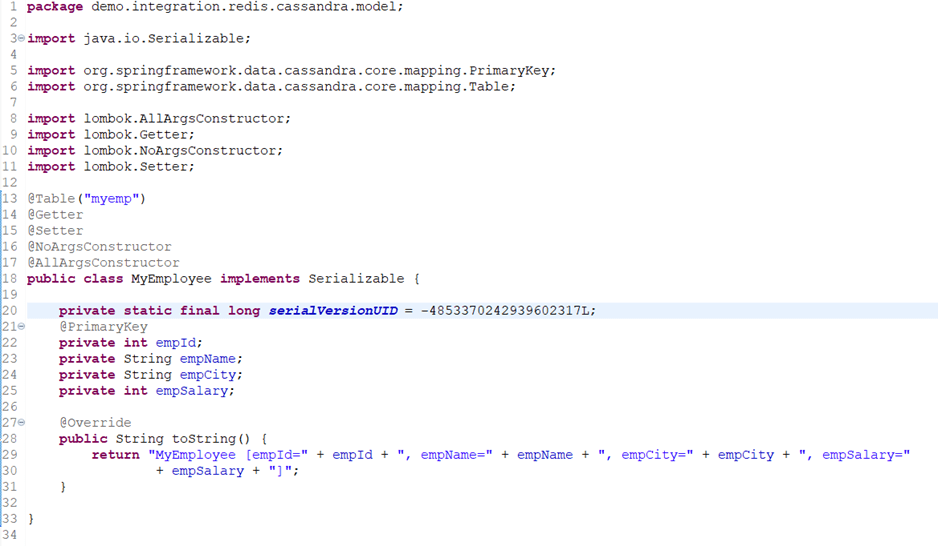
MyEmployee.java
@Table is Cassandra's annotation to map the table against the Java model class. When this annotation is not used the class name and table's name is considered same by default. In this example Lombok is used to generate the getter setter and constructors.
EmployeeService.java
Here, couple of methods have been defined, one to save the data into the database and the second one to fetch data from the database. These methods are invoked from the controller class.
EmployeeServiceImpl.java
@Cacheable is used to cache the retrieved data in Redis against the key and value pair as shown above. Note, data is not cached during insertion. This type of caching mechanism is known as Cache Miss or Lazy loading in which system first reaches out to the cache to get the data and when not found, subsequently reaches out to the database.
EmployeeRepository.java
The EmployeeRepository interface is extending the Cassandra Repository which internally extends Spring's native Crud Repository interface. This interface contains all the necessary methods for the CRUD operations.
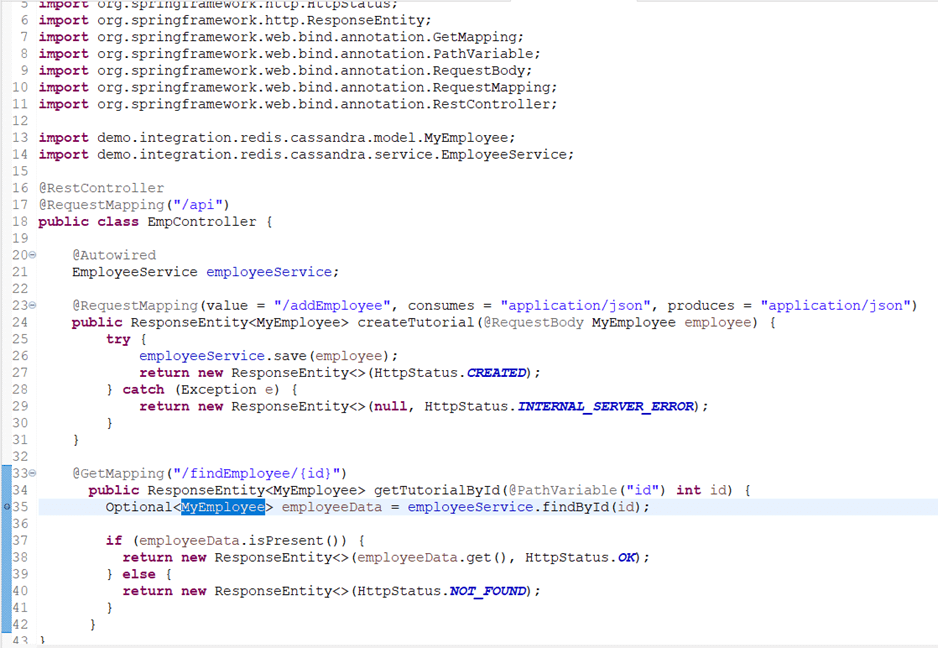
EmpController.java
The controller class of the application which exposes the rest endpoints.
How to test via Postman?
Step 1 - Execute the post method to insert a record in the database as shown below:
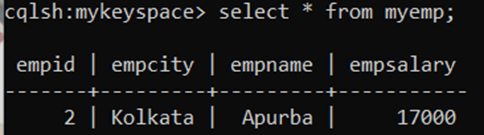
Verify the record in Cassandra
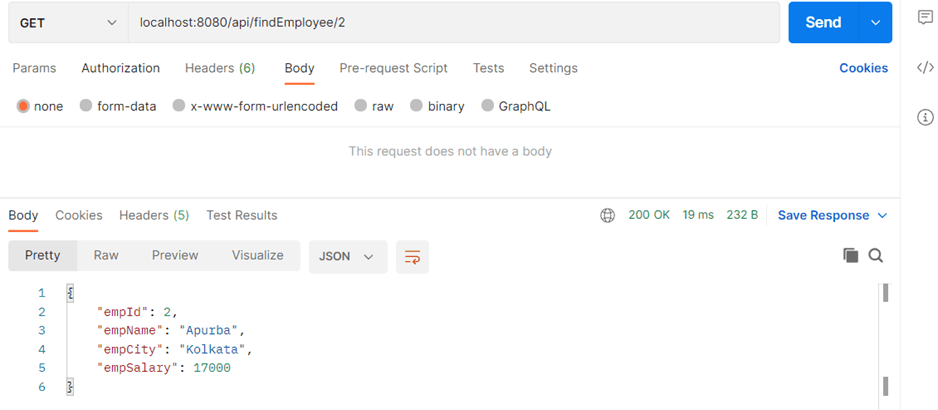
Step 2 – Next, execute the get method twice in succession to fetch the above inserted record.
1st execution and observation
The record is fetched from database and its corresponding SQL query is printed on the eclipse console. The record is persisted in the Redis Cache and can be verified in Redis CLI as shown below.
2nd execution and observation
No SQL query is printed on the console because the data is not hit as the record is available in Redis Cache and fetched from it. To further verify this claim, we can delete the key from Redis using the command "DEL key" and then re-execute the get request from Postman to fetch the data to observe that the query re-appears on the eclipse console which means the data is fetched from database and it is not available in Redis Cache.
Conclusion
This article gives an understanding of the basics of Redis Cache and how it can be integrated with Springboot and a database. We hope this article will help you get started on your Redis and Springboot journey.