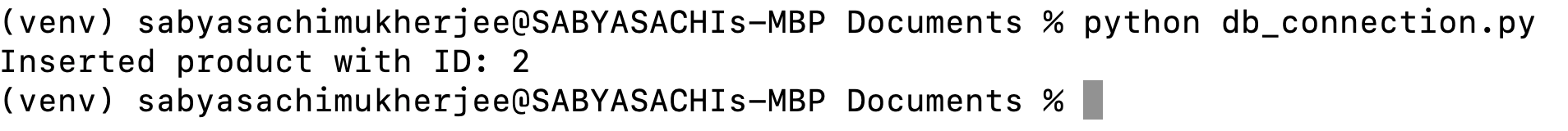Introduction
PostgreSQL provides two powerful data types for storing semi-structured data: JSON and JSONB. Combined with Python libraries such as psycopg2 or SQLAlchemy, we can efficiently store, query, and manipulate JSON documents directly within our database.
In this article. we will cover the following key concepts:
- JSON vs JSONB
- Creating tables with column type as JSON/JSONB
- Inserting JSON data from our python module
- Querying a JSON datatype column
- Updating nested JSON fields
- Indexing JSONB column for performance improvement
JSON vs JSONB
A JSON data type column will:
- store JSON data as it is
- be slower for querying because it needs to parse the text every time a query is made
- preserve the white spaces (if any) and the key order
A JSON data type column on the other hand will:
- store binary representation of the JSON data
- have the data pre-parsed which in turn helps in faster queries and helps in performance improvement
- support indexing (which we call as GIN, to be discussed later) which helps in faster searching
- not preserve the key order or any duplicate keys
Creating a table with JSONB datatype column
Here we will start our learning and understanding on JSONB data type and how we can use it in a real time scenario. As a first step, we will create a table with the name as products, which will have a column with data type as JSONB. For that, we will run the below create table query:
CREATE TABLE products (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
attributes JSONB,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
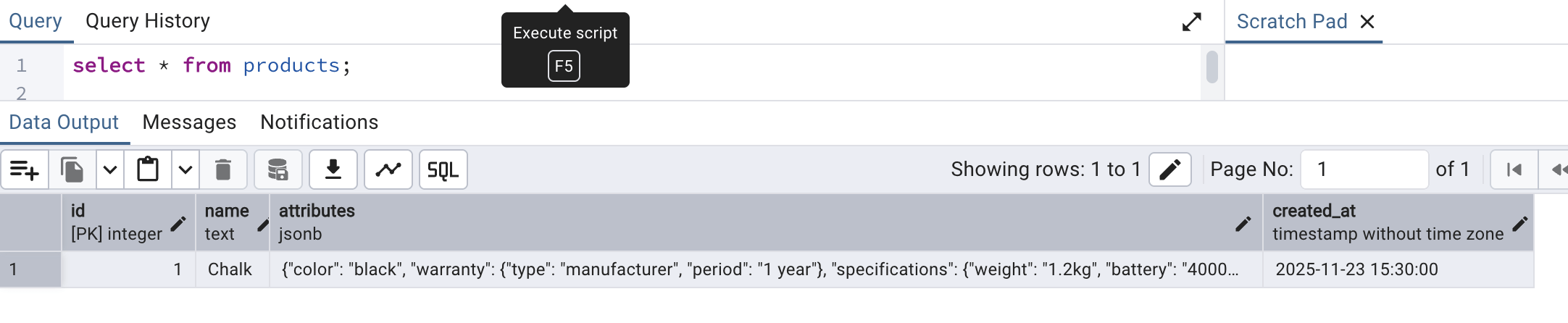
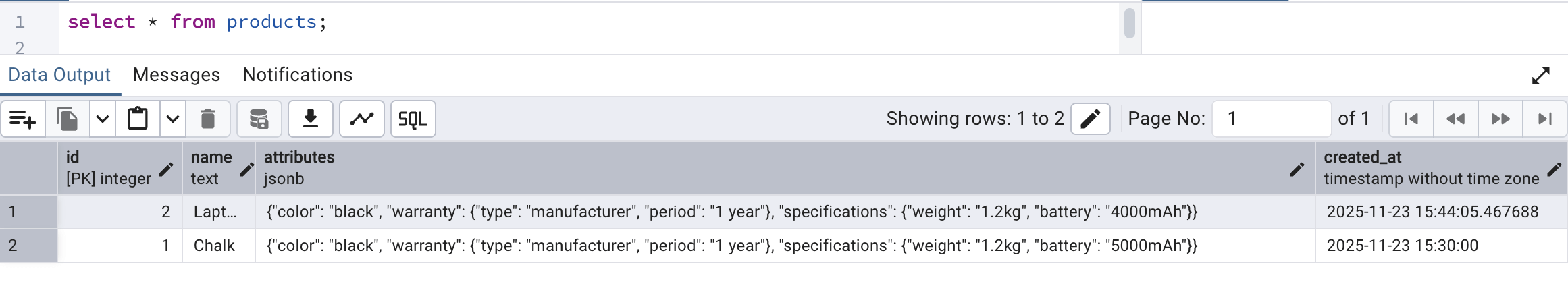
Now we will try to save/insert a data into this table from the SQL worksheet itself by running a static insert query to have a record into the table. For that, we will run the following query:
INSERT INTO PRODUCTS (name, attributes, created_at) values ('Chalk', '{
"color": "black",
"warranty": { "period": "1 year", "type": "manufacturer" },
"specifications": {
"weight": "1.2kg",
"battery": "4000mAh"
}
}
', '2025-11-23 15:30:00');Once the insertion is successful, we can see the record by running a select * query as follows:
Inserting JSON data from our python module
The first thing needed to insert JSON data from python module is to have a library installed called psycopg2. To install the same locally (if not installed already), run the following query:
pip install psycopg2
Once the installation is complete. we are all set to start working on establishing our connection from python module to our local PostgreSQL database.
In the sample code below we are importing the psycopg2 library, which will help us connect to our PostgreSQL database. We also import the json library since we will be dealing with JSON data. The remaining code snippet is self explanatory where we are just filling in the database connection details to establish a connection.
import psycopg2
import json
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname="local DB",
user="sabyasachimukherjee",
password="",
host="localhost",
port="5432"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()Save this file in your system as deb_connection.py and run the script from your preferred terminal and you should see no error message, which confirms that the connection was successful.
Now, we will try to expand the code here so that we can use this connection to store a real product information into the products table. For that, we have provided a code snippet below.
- The main function is the function that gets executed by default.
- Inside the main function, we are reusing the connection establishment code we used above.
- Next, we are creating the products data which is a pure JSON data.
- Then, we are preparing a INSERT query with placeholder to substitute the name and attributes of the product. This query will return the id of the product successfully inserted using this query.
- Finally, the query is executed when during execution, the name and the JSON data is passed. The JSON data is passed using json.dumps functions (the reason for which we imported the json library). json.dumps converts python dictionary to JSON string.
- The id of the new product successfully inserted is fetched and printed into the console.
import psycopg2
import json
def main():
try:
# -----------------------------
# Establishing connection to PostgreSQL
# -----------------------------
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname="local DB",
user="sabyasachimukherjee",
password="",
host="localhost",
port="5432"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# -----------------------------
# Preparing a set of data to insert
# -----------------------------
product = {
"color": "black",
"warranty": {"period": "1 year", "type": "manufacturer"},
"specifications": {"weight": "1.2kg", "battery": "4000mAh"}
}
# -----------------------------
# SQL Query to insert data
# -----------------------------
query = """
INSERT INTO products (name, attributes)
VALUES (%s, %s)
RETURNING id;
"""
# -----------------------------
# Execute insertion query to store the data
# -----------------------------
cursor.execute(query, ("Laptop", json.dumps(product)))
new_id = cursor.fetchone()[0]
conn.commit()
print(f"Inserted product with ID: {new_id}")
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", e)
finally:
# Clean-up
if cursor:
cursor.close()
if conn:
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
We will be saving this code as we wish (we are reusing the same file: db_connections.py) and then run the same file from terminal. We should see a following output:
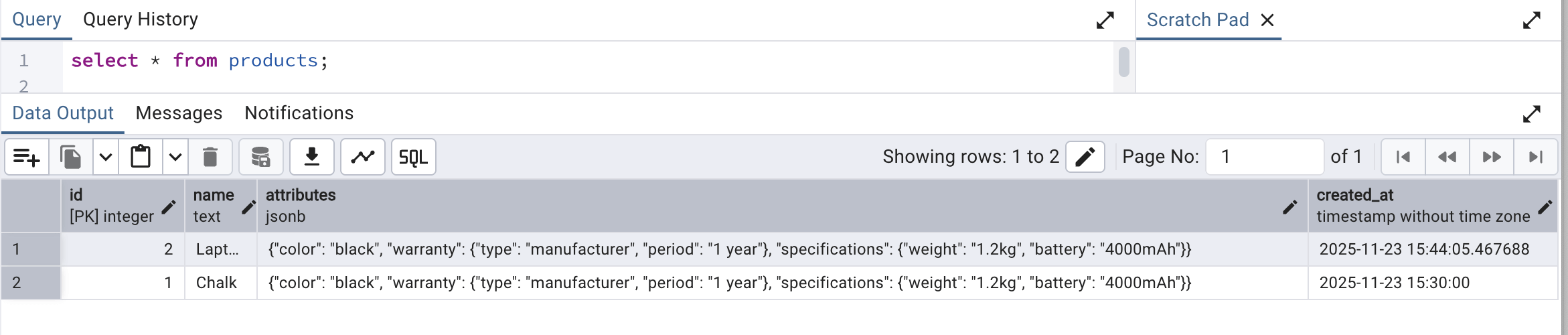
To confirm the same entry, we can head over to PGAdmin console and run a select query to check the same:
So, now we know how we can create a JSONB data type column in a table and populate the same with a JSON data from a python module.
Querying a JSON datatype column
Now that we have learnt on how to insert JSON data into the table, we will try to fetch JSON data from a JSONB column. For the same, we will use the following code snippet to fetch product information from the products table. This code does the following:
- Establishing the connection is already explained and understandeable.
- Next we write a query to just fetch the attributes column from the JSONB column of products table
- We are fetching all the rows from the products table
- Next, inside a for loop, we are printing each record retrieved
import psycopg2
import json
def main():
try:
# -----------------------------
# Connect to PostgreSQL
# -----------------------------
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname="local DB",
user="sabyasachimukherjee",
password="",
host="localhost",
port="5432"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# -----------------------------
# Execute Update Query
# -----------------------------
cursor.execute("SELECT attributes FROM products;")
rows = cursor.fetchall()
# -----------------------------
# Print fetched data
# -----------------------------
for row in rows:
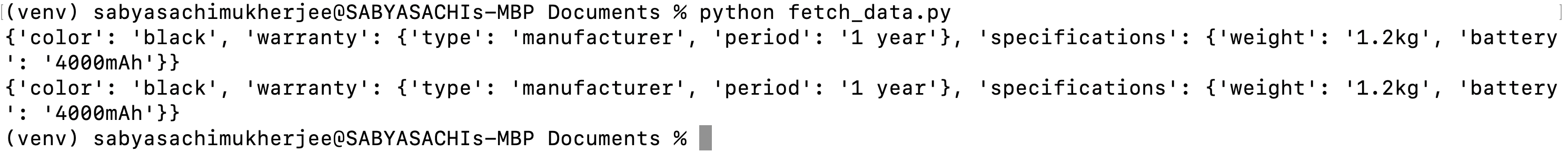
print(row[0])
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", e)
finally:
# Clean-up
if cursor:
cursor.close()
if conn:
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Once the file is saved and run from terminal, we should see a similar output:
But what if we want to fetch only the warranty of every product? In that case, we have to go inside each attribute's details and fetch only the warranty information. But to have that simplified, we can write the following query shown below. This code code does the following:
- Connection establishment steps are already known by now.
- Next, we are creating a query to fetch the name and warranty_period where we are mentioning that from attributes, the key warranty needs to be retrieved wherefrom the key period needs to looked upon and the value should be returned.
- Finally, we are printing the info for all the records fetched.
import psycopg2
import json
def main():
try:
# -----------------------------
# Connect to PostgreSQL
# -----------------------------
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname="local DB",
user="sabyasachimukherjee",
password="",
host="localhost",
port="5432"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# -----------------------------
# Execute Select Query
# -----------------------------
query = """
SELECT name, attributes->'warranty'->>'period' AS warranty_period
FROM products;
"""
cursor.execute(query)
rows = cursor.fetchall()
# -----------------------------
# Print fetched data
# -----------------------------
for row in rows:
print(row[0], 'has a warranty of', row[1], 'year(s)')
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", e)
finally:
# Clean-up
if cursor:
cursor.close()
if conn:
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Once executed from the terminal, we should see a similar output:
Now that we understood this, we might also get the idea that what if we need to apply some conditional checks on this JSONB data column and fetch only that record that satisfies the condition. For that, we will see an example now where we would fetch only that record from the products table for which certain criteria matches. We will fetch only those product(s) which has the color as black. To have this achieved, we will use the below code snippet.
After the connection is established, we are writing a query to fetch all product information where the attributes JSON data has an attributed named color which is equal to black.
import psycopg2
import json
def main():
try:
# -----------------------------
# Connect to PostgreSQL
# -----------------------------
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname="local DB",
user="sabyasachimukherjee",
password="",
host="localhost",
port="5432"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# -----------------------------
# Execute Select Query
# -----------------------------
cursor.execute("""
SELECT * FROM products
WHERE attributes->>'color' = %s
""", ("black",))
rows = cursor.fetchall()
# -----------------------------
# Print fetched data
# -----------------------------
for row in rows:
print(row)
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", e)
finally:
# Clean-up
if cursor:
cursor.close()
if conn:
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Once the above script is run, we should see a following output:
Note: Since the static insert data and also the python module inserted data, both has color as black, both are showing up here. If we change the color in the code from black to something else and rerun the script, we should see no records fetched.
Updating JSON fields
Now, we will try to update the JSON field values for an already existing record from our python module. We will use the below code snippet to do the same.
- After connection establishment, we are preparing to execute an update query where the attributes column will be updated with the new value provided as placeholder replacement against the battery field which is inside the specifications field within the attributes json.
- The update will happen for battery information against the record for which the product id matches to 1.
import psycopg2
import json
def main():
try:
# -----------------------------
# Connect to PostgreSQL
# -----------------------------
conn = psycopg2.connect(
dbname="local DB",
user="sabyasachimukherjee",
password="",
host="localhost",
port="5432"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
# -----------------------------
# Execute Update Query
# -----------------------------
cursor.execute(
"""
UPDATE products
SET attributes = jsonb_set(attributes, '{specifications,battery}', %s)
WHERE id = %s
""",
('"5000mAh"', 1)
)
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
print("Error:", e)
finally:
# Clean-up
if cursor:
cursor.close()
if conn:
conn.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
After the above script is run, no output will be generated but if we head over to PGAdmin, we should be able to compare that the battery information for product 1 before update was 4000mAh but it got changed to 5000mAh after the execution of the script.
Before script execution:
After the script execution:
Indexing JSONB column for performance improvement
We have very limited data for this tutorial purpose in the products database and so we will try to understand this conceptually. Just like we can add indices on columns in a database table, similarly, we can add index on JSONB data on PostgreSQL database. Since a JSONB data type column stores JSON data which contains of key and value, where value in turn can be another JSON structure, we can create index on JSON attribute/key. Index can be created in 2 ways for JSONB column:
- GIN (Generalized Inverted Index) on the entire JSON data,
- Index on a specific key of JSON data
To have an index on the entire JSON data, we can write a query like the one below.
- Naming the index as idx_products_attributes
- Using the entire attributes column value into it
- This index improves the contains search and also when we are searching for the existence of a specific key
CREATE INDEX idx_products_attributes ON products USING GIN (attributes);
Index on a specific key
To have an index on a specific key of the JSON data, we can have a query like the one below:
- The index is given a name as idx_color
- The indexing is being done on attributes column data which is a JSON data and the indexing will apply specifically to the color property of this JSON data.
- This improves search queries on color
CREATE INDEX idx_color ON products ((attributes->>'color'));
Conclusion
We finally learnt on how we can create a JSONB data type column in PostgreSQL database and use the same to persist, retrieve and filter JSON data from a python module. We also learnt some basic on applying index on such columns for faster search and performance improvement.