When you create a semantic model in Power BI desktop, you typically connect to one or more data sources (regardless of which mode you use, Import or DirectQuery). And naturally, you need to authenticate against those sources. In Power BI Desktop, you can use your own account (Microsoft Entra ID) or perhaps use SQL authentication (if possible).
But how will you authenticate after the semantic model has been published into a Power BI workspace? Surely you can’t keep using your own account, because if your account would ever be disabled, the refresh of the semantic model would stop. You could use another Microsoft Entra ID user as some sort of service account, but since Microsoft is pushing for users to have multi-factor authentication enabled, this might not be the best long-term solution.
Another option is the service principal (app registrations in Microsoft Entra ID), but this needs a secret and those expire after a while (and Microsoft has considerably shortened the lifetime of such a secret).
Lastly, if you’re connecting to SQL Server (or something related like Azure SQL DB), you can use SQL authentication (called “basic authentication” in the Power BI service, and “database authentication” in Power BI Desktop), but this is not recommended. Not all SQL instances have SQL authentication enabled, but this would also mean the SQL user name and the password would need to be shared between team members (anyone who needs to configure a data source connection in Power BI) and this might pose a security risk.
Fortunately, a new option has been added: workspace identity authentication. A workspace identity is an identity that is tied to a workspace in Microsoft Fabric (or Power BI). It’s very similar to a managed identity in Azure. With this workspace identity, you can connect your semantic models to (supported) data sources, but you can also use this method of authentication in Fabric data pipelines or in Fabric Dataflows Gen2.
The biggest advantage of the workspace identity is that it doesn’t have a password or secret. There’s nothing that can expire, nothing that can be leaked. It mitigates all the risks the other authentication options have. As long as the workspace exists, you can use its identity to connect to sources.
In this article, we’ll explore how you can use this workspace identity to connect to an Azure SQL DB from a Power BI semantic model.
Workspace Identity Authentication for a Semantic Model
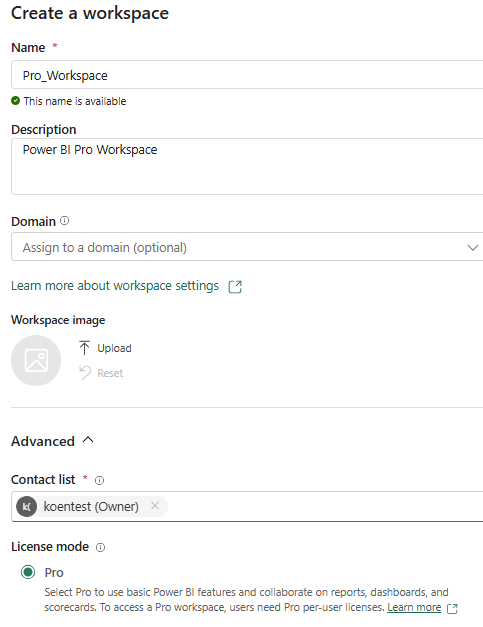
The first step is to create a workspace and enable workspace identity. To demonstrate that this new functionality also works in a Power BI Pro context, I’m creating a new Power BI Pro workspace:
Once the workspace is created, you can go to its settings and enable the workspace identity:
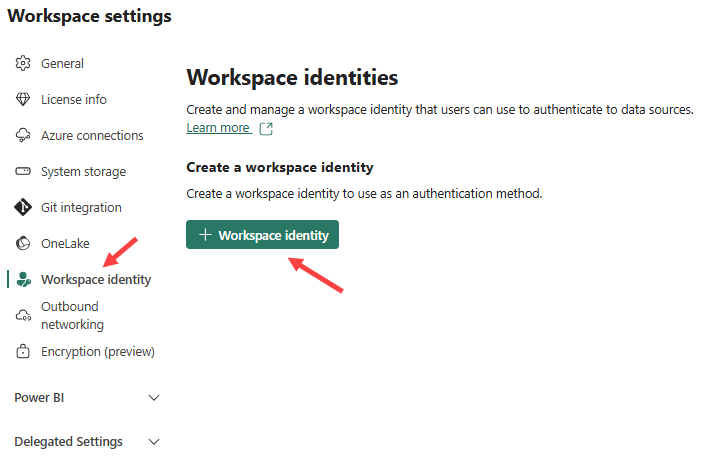
The identity will be created with the same name as the workspace itself.
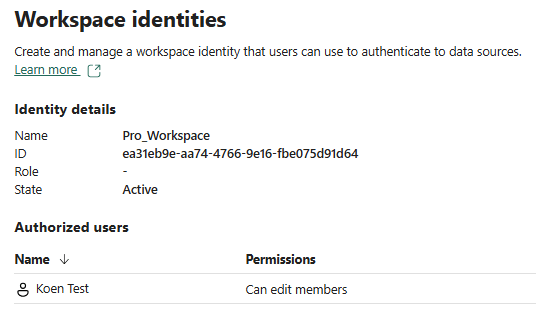
Behind the scenes, an enterprise application (and associated app registration) will be created in Microsoft Entra ID:
We also need a semantic model. I created a small model from data that is hosted in an Azure SQL DB.
Then I published the model to my Power BI Pro workspace.
When you go to the settings of the model, there’s an error message that the connection to the data source cannot be made, and you need to retry the credentials.
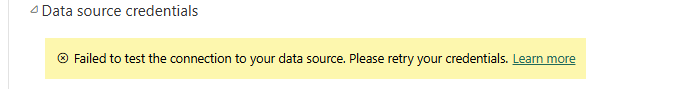
This is where you would specify the authentication method that the Power BI service will use when connecting the data source during a refresh, as described in the introduction. There are now two possible options:
- you can specify workspace identity authentication directly in the model settings
- you can create a shared cloud connection that uses workspace identity authentication and use that connection in the model
The last option has the benefit that the connection can be used in other places as well, such as other semantic models or Fabric Data Pipelines.
Before we can configure workspace identity authentication in the Power BI service, we need to do one last thing: make sure the identity actually has access to the database. Log into the database with SSMS (or your favorite database management tool) and open a new query. Execute the following SQL:
CREATE USER [My_Workspace] FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER; ALTER ROLE db_datareader ADD MEMBER [My_Workspace];
Replace [My_Workspace] with the name of your workspace.
Workspace Identity Authentication in the Semantic Model Settings
Go to the settings of the semantic model in your workspace:
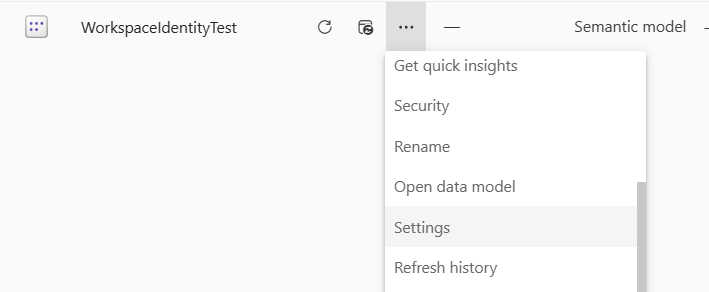
Click on Edit credentials in the Data source credentials section. For the Authentication Method, choose Workspace identity. Change the privacy level to what is needed in your organization and click Sign in.
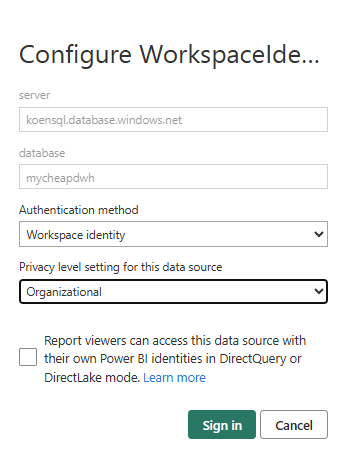
If you’ve given the workspace identity the correct permissions on your database, the data source credentials should now be saved, and the error should be gone.

And that’s it. Now let’s look at how we can create a reusable connection.
Workspace Identity Authentication in the Semantic Model Settings
In the Power BI service, go to Manage connections and gateways in the settings.
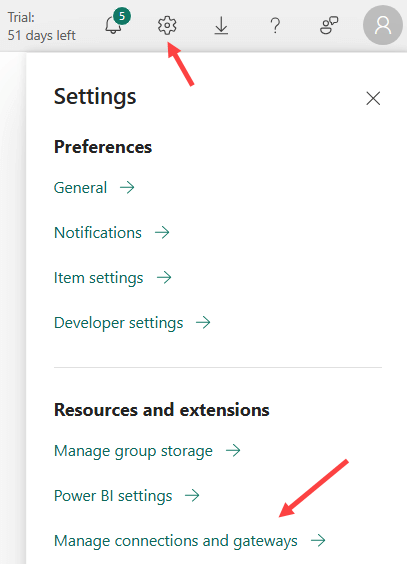
You’ll get an overview of all connections that already exist in your environment. In the top left corner, click New to create a new connection.
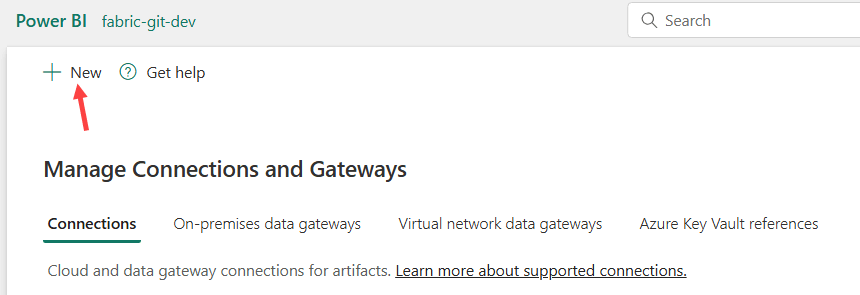
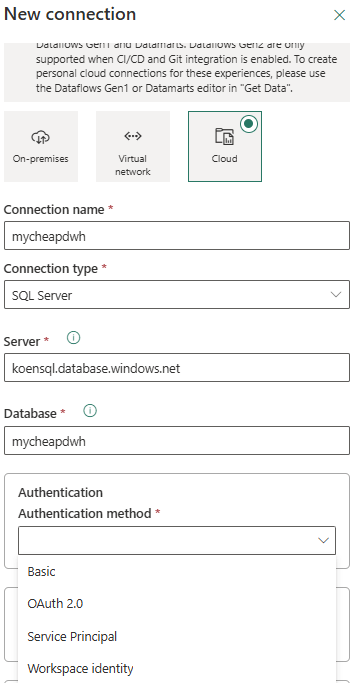
Choose Cloud as the source type, and SQL Server as the connection type. Specify a name for the connection and enter the server and database names. For the authentication method, choose Workspace identity.
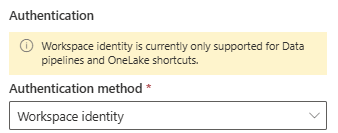
The following warning will be shown (at least while the feature is pretty new, as it will most likely be expanded into other Fabric objects):
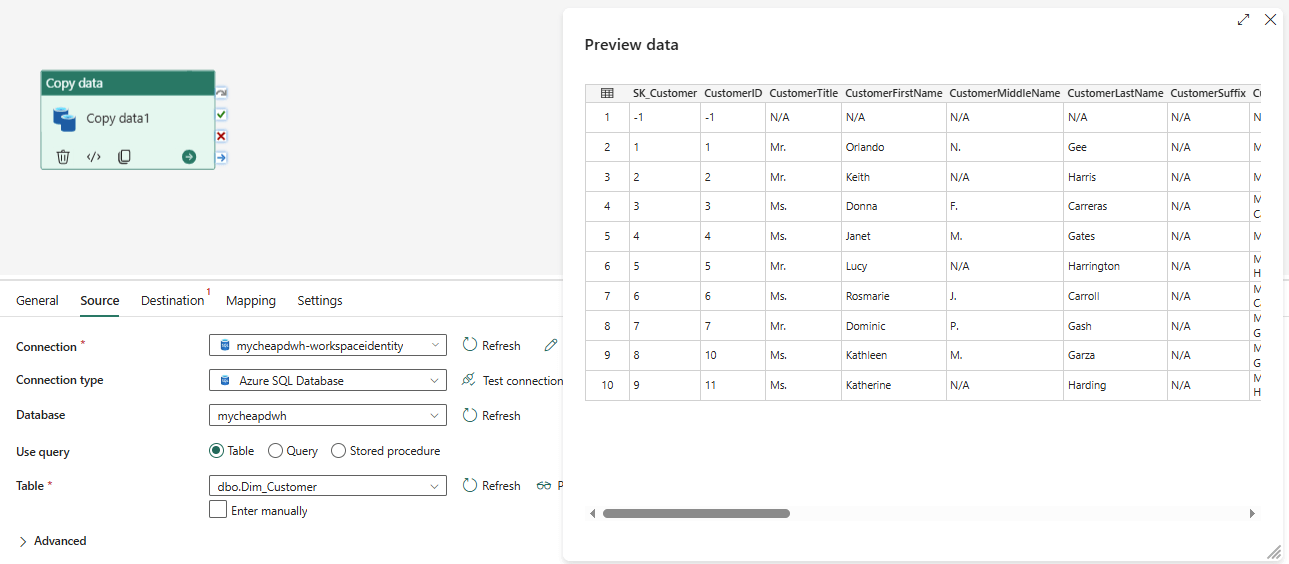
The warning doesn’t mention semantic models, but we can ignore this. After saving the connection, we can reuse it in multiple locations. For example, we can create a data pipeline and use this connection in a Copy Data Activity:
And of course we can use this connection in our semantic model. Instead of configuring the connection credentials in the Data source credentials section, we can use a shareable cloud connection:
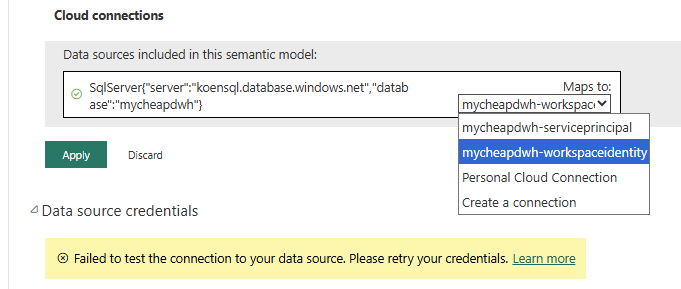
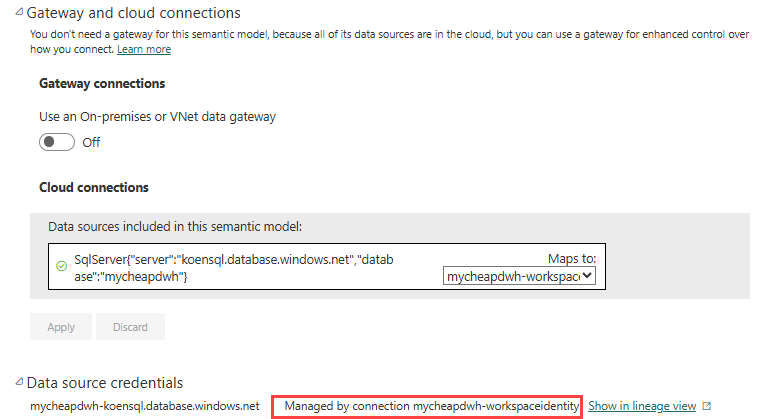
When you apply the cloud connection to the semantic model, you’ll see that the data source credentials are now managed by this connection.
To test it out, you can refresh the model in the service.
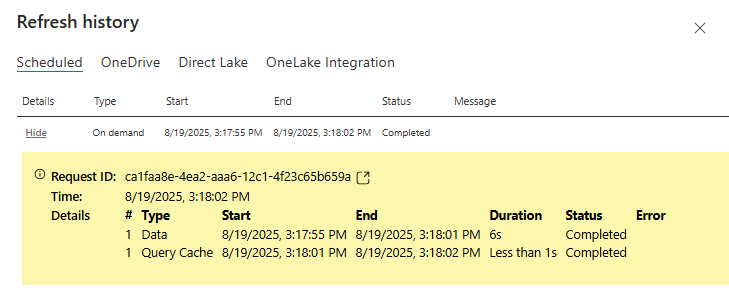
If everything is configured successfully, the refresh should finish without issues:
Conclusion
In this article we’ve shown you how you can authenticate against a (supported) source with a workspace identity. You can use this method directly in the data source credentials configuration of your semantic models, or you can create a shareable cloud connection that you can also reuse in other Fabric objects.
The advantage of using a workspace identity for authentication is that this identity doesn’t expire, and there’s no secret or password to manage.


