Setting page visibility and the active page are often overlooked last steps when publishing a Power BI report. It’s easy to forget the active page since it’s just set to whatever page was open when you last saved the report. But we don’t have to settle for manually checking these things before we deploy to a new workspace (e.g., from dev to prod). If our report is in PBIR format, we can run Fabric notebooks to do this for us.
You can download my notebook here. I’ll walk through the steps in this post.
Code Walkthrough
First, we must install semantic-link-labs. If you already have an environment with this library installed, you can use that and skip this step.
%pip install semantic-link-labsNext, we need to import some modules.
# Imports
import sempy_labs as labs
from sempy_labs import report
import ipywidgets as widgets
from IPython.display import displayThen we can get to work. First, I’m capturing the following information using widgets: workspace ID, report ID, and page name.
w_workspace = widgets.Text( description = 'Workspace ID',style={'description_width': 'initial'})
w_report = widgets.Text(description = 'Report ID', style={'description_width': 'initial'})
w_activepage = widgets.Text(description = 'Active Page Name', style={'description_width': 'initial'})
display(w_workspace)
display(w_report)
display(w_activepage)Running the code above will create 3 widgets. You will need to enter the required information into the widgets.
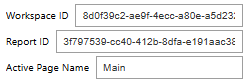
You could use variables in a cell to collect the required information. I’m using widgets to make it clear what information needs to be entered.
Once you have filled in the textboxes, you can run the last 2 cells. The fourth code cell is where I’m actually making the changes to the report.
var_reportname = labs.resolve_report_name(w_report.value, workspace=None)
var_rptw = labs.report.ReportWrapper(report=w_report.value, workspace=w_workspace.value,readonly=False)
var_rptw.set_active_page(w_activepage.value)
var_rptw.hide_tooltip_drillthrough_pages()
var_rptw.save_changes()
var_rptw.list_pages()First, I use the report ID entered into the widget to get the report name.
Then I create my report wrapper (var_rptw). This object will be used with all the subsequent functions.
Next I set the active page to the page name entered into the w_activepage widget using the set_active_page() function. Then I call hide_tooltip_drillthrough_pages().
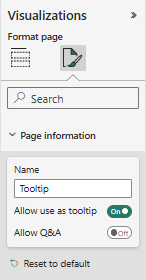
Each page has associated metadata that indicates whether it is a tooltip page and whether it is a drillthrough target page. I believe the tooltip page is determined by the page information setting labeled “Allow use as tooltip”.
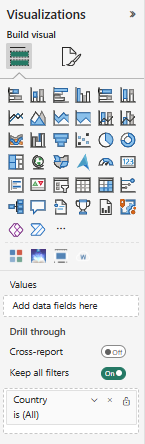
For drillthrough pages, I believe the presence of a field in the Drill through field well on the page is what causes it to be flagged as a drill through page.
Calling the set_active_page() and hide_tooltip_drillthrough_pages() functions changes the metadata for the report object, but we have to save the report changes back to the report in the target workspace, for the changes to take effect. This is why we call var_rptw.save_changes().
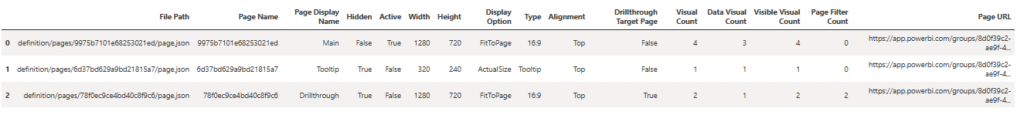
Once we save the changes, we get a response back that lists the changes made to the report.

Calling list_pages() produces a pandas DataFrame with metadata for each page. We can refer to the Hidden, Active, Type, and Drillthough Target Page columns to confirm the desired changes.
As a final confirmation, we can also view the Power BI report from within the notebook. That is what I’m doing with the launch_report() function. It provides a read-only view of the report in the notebook cell output..
More posts about Semantic Link Labs
So far, I’ve been exploring the report and admin subpackages of Semantic Link Labs. Below are some other blog posts I’ve written about them.
Finding fields used in a Power BI report in PBIR format with Semantic Link Labs
Get Power BI Report Viewing History using Semantic Link Labs
Happy reading!
The post Modify Power BI page visibility and active status with Semantic Link Labs first appeared on Data Savvy.

