Difference between RAID 0 and RAID 1+0
-
August 20, 2018 at 12:47 pm
What is the difference between this two?
-
August 20, 2018 at 12:59 pm
-
August 20, 2018 at 1:05 pm
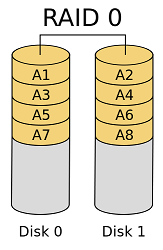
elea.grig - Monday, August 20, 2018 12:47 PMWhat is the difference between this two?Raid 0 RAID 0 (also known as a stripe set or striped volume) splits ("stripes") data evenly across two or more disks, without parity information, redundancy, or fault tolerance. Since RAID 0 provides no fault tolerance or redundancy, the failure of one drive will cause the entire array to fail; as a result of having data striped across all disks, the failure will result in total data loss. This configuration is typically implemented having speed as the intended goal.[2][3] RAID 0 is normally used to increase performance, although it can also be used as a way to create a large logical volume out of two or more physical disks. RAID 0 can be created with disks of differing sizes, but the storage space added to the array by each disk is limited to the size of the smallest disk.

Raid 1 is mirrored so a file will exist in more than one disk and can recover from a disk failure. This has slow write performance as the file has to be written to two disks.
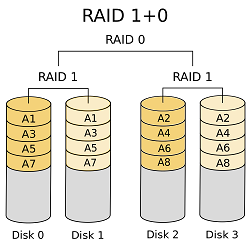
Raid 1+0, also called RAID 10 and sometimes RAID 1&0, is similar to RAID 01 with an exception that two used standard RAID levels are layered in the opposite order; thus, RAID 10 is a stripe of mirrors.
RAID 10, as recognized by the storage industry association and as generally implemented by RAID controllers, is a RAID 0 array of mirrors, which may be two- or three-way mirrors,[6] and requires a minimum of four drives. However, a nonstandard definition of "RAID 10" was created for the Linux MD driver; Linux "RAID 10" can be implemented with as few as two disks. Implementations supporting two disks such as Linux RAID 10 offer a choice of layouts. Arrays of more than four disks are also possible.
In most cases RAID 10 provides better throughput and latency than all other RAID levels except RAID 0 (which wins in throughput). Thus, it is the preferable RAID level for I/O-intensive applications such as database, email, and web servers, as well as for any other use requiring high disk performance. 1+0 is often the choice for storing database files.
-
August 20, 2018 at 1:34 pm
Jonathan AC Roberts - Monday, August 20, 2018 1:05 PMelea.grig - Monday, August 20, 2018 12:47 PMWhat is the difference between this two?Raid 0 is striped so a file will be split across more than one disk
Raid 1 is mirrored so a file will exist in more than one disk and can recover from a disk failure. This has slow write performance as the file has to be written to two disks.
Raid 0+1 is stripped across at least 3 disks with parity info so that a file can be recovered if there is a single disk failure. This offers performance and recovery, whereas Raid 0 offers no recovery on a disk failure and Raid 1 does not perform as well as Raid 0. This is often chosen for storing database files.Nope, your Raid 0 + 1 definition is wrong. There is no parity bit in Raid 0 + 1 or Raid 1 + 0 and they are different.
-
August 20, 2018 at 1:37 pm
Check this link: https://www.diffen.com/difference/RAID_0_vs_RAID_1
-
August 20, 2018 at 2:02 pm
Lynn Pettis - Monday, August 20, 2018 1:37 PMCheck this link: https://www.diffen.com/difference/RAID_0_vs_RAID_1Thanks, I'll update my answer.
Viewing 6 posts - 1 through 5 (of 5 total)
You must be logged in to reply to this topic. Login to reply