SQL Server 2017 is the first version of SQL Server that will also run natively on Linux and on macOS via Docker. There has never been a quicker way to get SQL Server installed and running in a development environment than using this new Docker image.
This is a video of the whole process which on a slow connection and an old MacBook air takes 4 minutes and 7 seconds (This is amazing!)
Let’s run through these steps, you’ll need to have Docker installed to follow along.
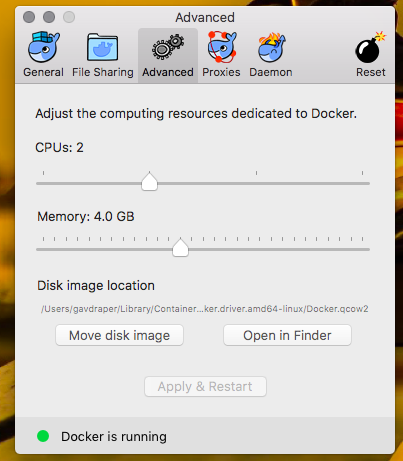
Change the Docker settings to use 4gb of RAM as this is a requirement for SQL Server. To do this right click the Docker icon in the menu bar, click preferences and on the advanced tab change RAM to 4gb. Once set click the apply & restart button then wait for Docker to restart.

Run the following command to pull down the SQL Server Docker image
docker pull microsoft/mssql-server-linux
Now we just need to run this image. Let’s also mount a volume so any data we create gets persisted between container restarts this is done by including the -v argument in the Docker run command…
Docker run -e ‘ACCEPT_EULA=Y’ -e ‘SA_PASSWORD=(Str0ngP4ss)’ -p 1433:1433 -v sqlvolume:/var/opt/mssql -d microsoft/mssql-server-linux
Let’s break down what this command is doing…
- -e ‘ACCET-EULA=Y’ : This accepts the EULA and without this SQL Server will not start. This is normally done in the UI For the SQL Server installer but in this case as there is no installer it’s done in the Docker Run command.
- -e ‘SA_PASSWORD=(Str0ngP4ss)’ = : Here we specify the SA account password that we will use to connect to this server.
- -p 1433:1433 : This publishes port 1433 on the container to port 1433 on the host to allow us to connect to SQL Server.
- -v sqlvolume : This tells our container to mount a volume so we can store files in that path and they will be stored on the host to survive restarts of the container (By default containers persist no data and will start in a clean state every time)
At this point we now have a SQL Server instance running in our new container. On macOS the best ways to connect to this are either via VS Code wth the MSSQL extension or SqlCmd for a command line option. Whichever tool you choose you just need to point it to localhost with a username of sa and a password of whatever you specified in your Docker Run command.
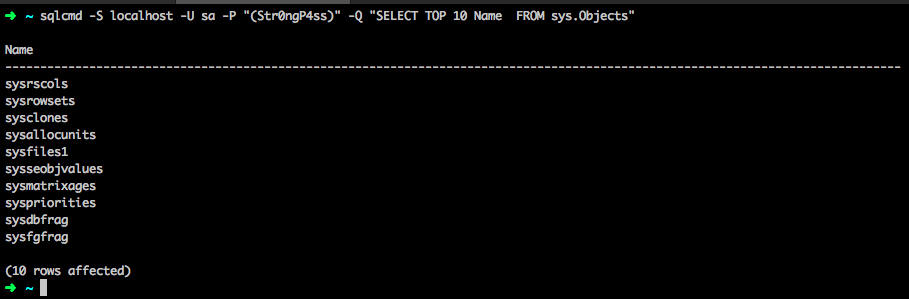
For example if you have sqlcmd installed from the link above you can run the following command to query our new SQL Server 2017 instance running inside of docker.
sqlcmd -S localhost -U sa -P “(Str0ngP4ss)” -Q “SELECT TOP 10 Name FROM sys.Objects”